Hair loss is a common and troubling problem caused by a complex range of factors including genetics, hormones, trauma, and iatrogenic events. About 160 million people in China alone suffer from hair loss. Currently, there are several treatment options for hair loss patients, such as using oral or topical medications, or undergoing surgical treatment. However, these treatment methods have limitations, as drug therapy can only provide temporary relief of symptoms, and hair may start to fall out again when patients stop taking medication. For example, oral administration of finasteride has side effects and can be teratogenic. After stopping the medication, hair loss will accelerate.
The use of autologous single hair follicles and hair follicle unit transplantation is a reliable surgical treatment method, but the number of hair follicle donors is limited, and hair follicle transplantation has a low survival rate and high cost, which can cause great pain to patients. Therefore, there is an urgent need for new treatment methods for hair loss. Numerous studies have found that stem cells have significant effects on hair regeneration and hair loss prevention, bringing hope and hope to hair loss patients.
Hair loss is an inflammatory cytokine mediated disease
The pathogenesis of hair loss is closely related to signal transduction mediated by Th-1 and NKG2D. Research has shown that hair follicles are immune immune immune sites. When the immune immunity of hair follicles collapses, CD4 and CD8 T cells, as well as some natural killer cells, gather around the self antigens of the hair follicles and can lead to hair loss. Stem cells have immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects. Scientists injected stem cells intravenously into depilated rats and found that they can inhibit the production of IFNG, CXCL9, and CXCL10, as well as the infiltration of NKG2D+T cells, effectively preventing hair loss.
Stem cells can secrete a large amount of growth factors
Such as keratinocyte growth factor, vascular epithelial growth factor, platelet growth factor, and hepatocyte growth factor. These growth factor proteins play an important role in promoting hair regeneration. Futuremed Clinic has shown significant efficacy in treating male and female hair loss after reinfusion of autologous adipose stem cells into patients. Futuremed Clinic experts injected stem cell conditioned medium microneedles subcutaneously into patients, and after a few weeks, the patient's hair density and thickness increased significantly without any toxic side effects.
The ability of stem cell transplantation to promote hair regeneration is greatly enhanced
Stem cells and their conditioned medium can promote hair regeneration and prevent hair loss. Compared to hair follicle transplantation, stem cell therapy for hair loss has the advantages of convenience, safety, significant effectiveness, simple treatment process, and high patient acceptance, which provides an alternative treatment method for hair loss patients.
Characteristics of hair follicle stem cells and their relationship with hair regeneration
Hair follicle stem cells are a type of multipotent cell located in the protuberance of the outer root sheath of human hair follicles. Hair follicle stem cells belong to adult stem cells, which have slow periodicity and remain in a quiescent state in the body. Under the influence of the living environment, they exhibit astonishing proliferation ability. Research has found that hair follicle stem cells have multi-directional differentiation potential and can differentiate into epidermis, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and participate in the process of skin wound healing.
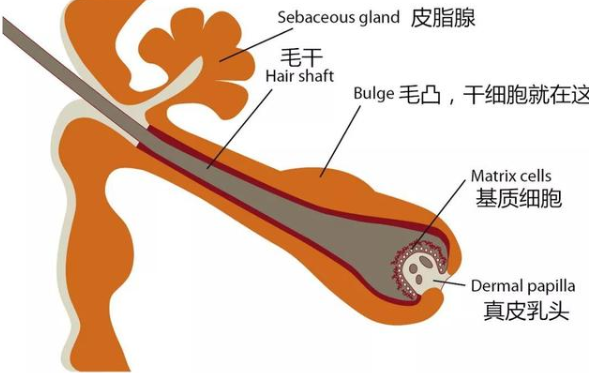
Hair follicle stem cells are primitive cells in hair follicles, which, like other adult stem cells, have characteristics such as slow periodicity, undifferentiated nature, self-renewal, and strong in vitro proliferation ability. The differentiation of hair follicle stem cells goes through three stages: hair follicle stem cells (FSC), transient amplifying sales (TAC), and postmitotic differentiating sales (PDC). Hair follicle stem cells appear cubic under light microscopy, with small cell volume, high nuclear cytoplasmic ratio, smooth surface, few wrinkles, and are also known as non serrated cells. The increase in cell volume is negatively correlated with proliferation ability. The ultrastructure shows that there are a few microvilli on the cell surface, many curled nuclei, and dispersed chromatin, all of which exhibit the characteristics of primitive cells.
Hair follicle stem cells have high proliferation potential and exhibit clonal growth when cultured in vitro. They can induce differentiation into neurons, glial cells, smooth muscle cells, melanocytes, etc. When implanted in vivo, they can differentiate into neurons, melanocytes, and keratinocytes.
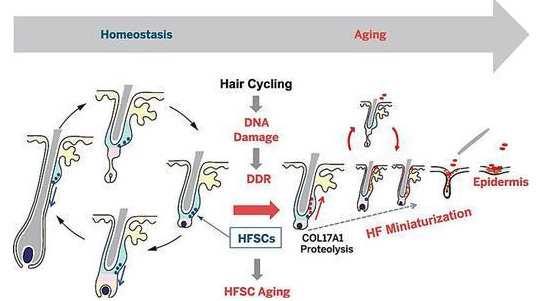
Researchers from Yale University in the United States have found that patients with seborrheic alopecia still have stem cells at the root of their hair follicles, and all they need to do is find the stimulating signals that cause their hair to grow. When hair stops growing, the fat layer in the scalp shrinks. And when hair starts to grow, the fat layer will grow again. This process is called "fat generation", and during the regrowth of the fat layer and hair regeneration, a type of stem cell that can produce fat precursors plays an important role. These cells produce PDGF molecules, which promote hair regeneration.
The three core technologies of stem cell and extracellular vesicle hair regeneration are: maintaining balance, promoting regeneration, regulating the microenvironment of scalp cells, balancing scalp oil, microbiota, metabolic balance, reshaping scalp resistance barriers, and using plant small molecule penetration technology to penetrate layer by layer into the dermis layer of the scalp, restoring the normal physiological functions of aging and problematic hair follicles, endowing dermal cells with sufficient nutrients, applying regenerative medicine technology to prepare cell active factors for hair regeneration, promoting hair follicle stem cell differentiation, accelerating hair cell division, supplying full layer cell nutrition, promoting hair regrowth, and more accurately achieving targeted promotion of hair follicle stem cell growth, effectively achieving hair regrowth.
